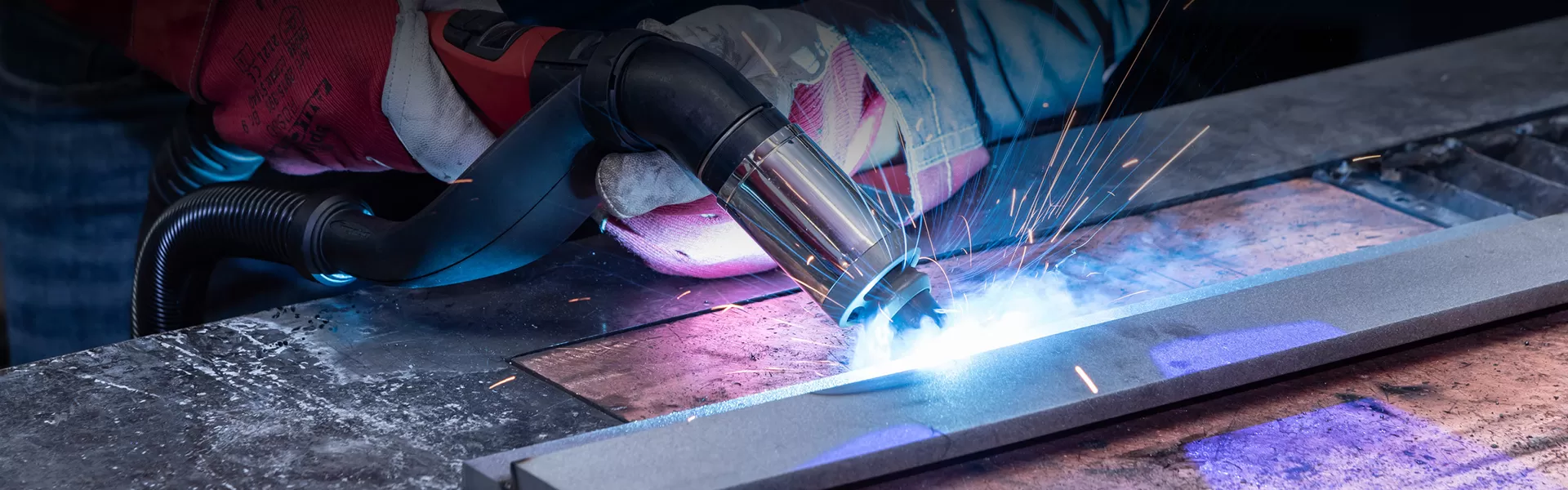
Gas-shielded welding is a welding method that utilizes gas to protect the arc and the molten pool to achieve the joining of metal materials. According to the type of shielding gas used, gas shielded welding can be divided into CO2 shielded welding, argon shielded welding and mixed gas shielded welding. Due to its high welding quality, high efficiency, as well as wide applicability, gas shielded welding has been very widely used in modern industry.
The welding position in gas shielded welding refers to the orientation of the weld in space, which is crucial for the selection of welding process.
Different welding positions will directly affect welding quality, penetration depth, weld appearance and welding efficiency. Next, we will discuss in detail several typical welding positions of gas shielded welding, including their respective advantages and disadvantages as well as applicable scope.
1. Flat welding position
The flat welding position refers to the weld being on a horizontal plane or at an angle of less than 15° to the horizontal plane. This position is the most commonly used and easiest to control position in gas shielded welding. The main advantages of flat welding include:
(1) Stable molten pool: Less affected by gravity and easier to maintain the stability of the molten pool.
(2) Well-formed welds: Welds usually have a nice appearance and uniform penetration.
(3) Fast welding speed: Due to the simple operation, the welding efficiency is relatively high.
(4) Less spatter and pores: Better operating conditions, which helps reduce welding defects.
However, flat welding also has some limitations:
(1) Weld width limitation: The weld width is limited by the thickness of the weldment, and wider welds cannot be obtained.
(2) Relatively low strength and toughness: Due to the narrow weld, its strength and toughness may not be as good as other welding positions.
Flat welding is widely used in many applications, such as the welding in construction industry and mechanical equipment, etc.
2. Horizontal welding position:
Horizontal welding position means that the weld is located on the vertical plane, or at an angle of less than 15° to the vertical plane. This welding position is relatively difficult and requires the welder to have a higher technical level. The advantages of horizontal welding are:
(1) Wide weld width: A wider weld can be obtained, which is suitable for welding thicker workpieces.
(2) Enhanced welding strength: The strength and toughness of welds are relatively high, making them suitable for structures that can withstand larger loads.
However, the horizontal welding position also brings some challenges:
(1) The molten pool is susceptible to gravity: The molten pool may flow and increase instability.
(2) Slower welding speed: The operation is complicated and requires careful control, resulting in a decrease in speed.
(3) Increased risk of defects: The probability of spatter and pores is higher.
Horizontal welding is often used for welding valves, pipes and large equipment.
3. Vertical welding position:
Vertical welding position means that the weld is located in the vertical plane or at an angle greater than 15° to the vertical plane. This position is one of the most complex in welding and usually requires advanced technology. The advantages of vertical welding are as follows:
(1) High weld strength: Welds with higher strength and toughness can be obtained, suitable for thin material welding.
(2) High precision requirements: Suitable current and welding speed can produce high-quality welds.
On the other hand, it also faces many challenges:
(1) Poor molten pool stability: It is relatively easy to flow, affecting the formation.
(2) Slow welding speed: The difficulty of controlling the molten pool makes the entire process time-consuming.
(3) High defect risk: If the heat input is not well controlled, defects such as pores or incomplete penetration may occur.
·
Vertical welding is common in long welds or welding workpieces required high-strength welding, especially in the welding of structural parts and thin plates.
4. Overhead welding position
The overhead welding position refers to the welding position where the weld is located below the horizontal plane, or at an angle greater than 15° to the horizontal plane. This type of welding is considered to be a more difficult welding operation due to its characteristics, and usually requires the welder to have a higher level of skill and rich experience. The main advantages of overhead welding include:
(1) Larger weld width: Wider welds can be achieved, suitable for welding thicker workpieces.
(2) High strength and toughness of the weld: When the welding parameters are reasonably adjusted, the strength and toughness of the weld will be effectively improved.
Although overhead welding has its advantages, it also has some notable disadvantages:
(1) The molten pool is easily affected by gravity: Due to the particularity of the welding direction, the molten pool is more likely to flow, which may lead to poor weld formation.
(2) Slow welding speed: The overhead welding position is complicated to operate and requires welders to be more careful and meticulous, so the overall welding speed is usually slower.
(3) Many pores and spatters: During overhead welding, due to gravity of the molten pool, the probability of spatter and pores increases, which may affect the welding quality.
4. Overhead welding position:
The overhead welding position refers to the welding position where the weld is located below the horizontal plane, or at an angle greater than 15° to the horizontal plane. This type of welding is considered to be a more difficult welding operation due to its characteristics, and usually requires the welder to have a higher level of skill and rich experience. The main advantages of overhead welding include:
Larger weld width: Wider welds can be achieved, suitable for welding thicker workpieces.
High strength and toughness of the weld: When the welding parameters are reasonably adjusted, the strength and toughness of the weld will be effectively improved.
Although overhead welding has its advantages, it also has some notable disadvantages:
The molten pool is easily affected by gravity: Due to the particularity of the welding direction, the molten pool is more likely to flow, which may lead to poor weld formation.
Slow welding speed: The overhead welding position is complicated to operate and requires welders to be more careful and meticulous, so the overall welding speed is usually slower.
Many pores and spatters: During overhead welding, due to the influence of gravity of the molten pool, the probability of spatter and pores increases, which may affect the welding quality.
Overhead welding is widely used in workpieces with complex or thick structures that need to be welded, such as the welding of the substructure of large equipment and the ships.
5. Conclusion
On the whole, gas shielded welding is an efficient welding method with a wide range of applications. However, when performing gas shielded welding, choosing the right welding position is critical. The four typical welding positions - flat welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding and overhead welding - each have their own unique advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different welding occasions and requirements.
1-Flat welding is suitable for most welding scenarios, with simple operation and fast welding speed, but the strength of the weld may be limited.
2-Horizontal welding is suitable for thick parts connection and can provide better weld quality, but the operation is more complicated.
3-Vertical welding requires a high technical level and is suitable for thin material welding, but it is difficult to control and prone to welding defects.
4-Although overhead welding has a considerable weld width, the molten pool is greatly affected by gravity and is the most difficult to operate.
In actual welding, welders should select appropriate welding positions according to specific welding requirements and workpiece characteristics, and reasonably adjust welding parameters to ensure welding quality and structural safety. Proper use of gas shielded welding skills and processes will bring significant benefits and effects to the welding work.